Ultrasound images of Acute pyelonephritis
Acute inflammation of the kidney rarely results in any ultrasound abnormality. Occasionally the kidney may be enlarged and hypoechoic, the contrast between the kidney and the hepatic or splenic parenchyma increasing due to oedema, but the ultrasound changes are generally subtle. The normally clear differentiation between the cortex and the medullary pyramids may become indistinct, but again may go unrecognized.
CT is useful for detecting subtle inflammatory changes within the kidney. Ultrasound images Chronic pyelonephritis This chronic inflammatory state is usually the result of frequent previous inflammatory/infective episodes. The kidney may be small and often has focal scarring present. Scar tissue has the appearance of a hyperechoic, linear lesion which affects the smooth renal outline and crosses the renal cortex (Fig. ultrasound images below).
CT is useful for detecting subtle inflammatory changes within the kidney. Ultrasound images Chronic pyelonephritis This chronic inflammatory state is usually the result of frequent previous inflammatory/infective episodes. The kidney may be small and often has focal scarring present. Scar tissue has the appearance of a hyperechoic, linear lesion which affects the smooth renal outline and crosses the renal cortex (Fig. ultrasound images below).
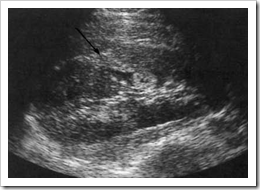
Ultrasound images Cortical scar tissue is demonstrated following repeated episodes of urinary tract infection.
(Do not confuse focal scarring with fetal lobulation: the latter is smooth, thin, continuous with the capsule and forms an indentation between the pyramids.) The renal cortex is frequently thin in chronic pyelonephritis and may appear abnormally hyperechoic. Bladder diverticula Repeated infections can cause the bladder wall to thicken and become trabeculated. In such cases, a bladder diverticulum may form, making treatment of subsequent infections particularly difficult. The diverticulum may harbour debris or stones and may fail to empty properly, often enlarging as the urine refluxes into it when the patient micturates (Fig. ultrasound images below).

Ultrasound images A bladder diverticulum can be seen communicating with the bladder (arrow). The main bladder wall is trabeculated.
LiveJournal Tags: Ultrasound images of Acute pyelonephritis
Post a Comment for "Ultrasound images of Acute pyelonephritis"