Ultrasound images Haemodynamics vascular tree of the kidney
The vascular tree of the kidney can be effectively demonstrated with colour Doppler (Fig. below).

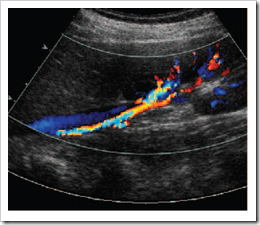
TS through the LK demonstrates the main renal vein (blue) draining into the IVC. The main
renal artery can be seen in red alongside.
renal artery can be seen in red alongside.
TS through the LK demonstrates the main renal vein (blue) draining into the IVC. The main
renal artery can be seen in red alongside
renal artery can be seen in red alongside
ultrasound images The waveform from the main renal artery at the hilum of the kidney is of
low resistance with good end-diastolic flow. The spectrum from the adjacent vein can be seen below the baseline.
low resistance with good end-diastolic flow. The spectrum from the adjacent vein can be seen below the baseline.
By manipulating the system sensitivity and using a low pulse repetition frequency (PRF), small vessels can be demonstrated at the periphery of the kidney. Demonstration of the extrarenal main artery and vein with colour Doppler is most successful in the coronal or axial section by identifying the renal hilum and tracing the artery back to the aorta or the vein to the inferior vena cava (IVC). The best Doppler signals, that is, the highest Doppler shift frequencies, are obtained when the direction of the vessel is parallel to the beam, and taken on suspended respiration. The left renal vein is readily demonstrated between the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and aorta by scanning just below the body of the pancreas in transverse section. The origins of the renal arteries may be seen arising from the aorta in a coronal section [Fig. below]. The normal adult renal vasculature is of low resistance with a fast, almost vertical systolic upstroke and continuous forward end diastolic flow. Resistance generally increases with age. The more peripheral arteries are of lower velocity with weaker Doppler signals, and are less pulsatile than the main vessel.
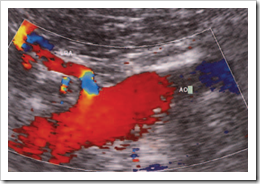
Ultrasound images Coronal section through the aorta (AO) showing the origin of the left renal artery. The blue colour in the proximal section of the artery is an aliasing artefact due to the strong Doppler signal from this part of the vessel, which is parallel to the beam. (Compare this with the aorta, which, because of its relatively perpendicular angle with the beam, has a poor Doppler signal, despite its high velocity in reality.)

Post a Comment for "Ultrasound images Haemodynamics vascular tree of the kidney"