Puborectalis Syndrome
Gastrointestinal tract images Puborectalis syndrome is used to describe incomplete relaxation or paradoxical contraction of the puborectalis muscle during evacuation, often with resultant outlet obstruction. At times an isolated finding, it is one of a spectrum of abnormalities detected in constipated patients. The term pelvic floor dyssynergy is used by some to encompass a more complex set of findings.
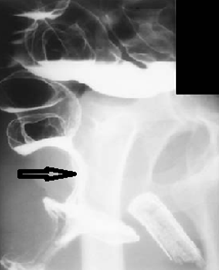
Primary symptom of puborectalis syndrome consists of incomplete or intermittent evacuation. Voiding proctography reveals an abnormal puborectalis muscle impression along the posterior rectal wall, a reduced change in anorectal angle during straining, and prolonged barium pooling in the rectal ampulla; manometry detects an increase in external anal sphincter pressure under straining in about two thirds of these patients. Some patients also have associated rectal mucosal prolapse and a rectocele.
Primary symptom of puborectalis syndrome consists of incomplete or intermittent evacuation. Voiding proctography reveals an abnormal puborectalis muscle impression along the posterior rectal wall, a reduced change in anorectal angle during straining, and prolonged barium pooling in the rectal ampulla; manometry detects an increase in external anal sphincter pressure under straining in about two thirds of these patients. Some patients also have associated rectal mucosal prolapse and a rectocele.
This is radiology images of Nonrelaxing puborectalis muscle (arrow). This is a contributing factor in solitary rectal ulcer syndrome.
Post a Comment for "Puborectalis Syndrome"