CT urography
Until recently, intravenous urography (IVU) or excretory urography was used as the traditional imaging technique for the radiologic evaluation of the kidneys, pelvicaliceal systems, ureters, and bladder. IVU has lower sensitivity in detecting small renal masses and can detect only 21% of masses smaller than 2 cm, 52% of masses between 2 and 3 cm, and 82% of masses 3 cm or larger . Noncontrast CT has 97% sensitivity and 96% specificity for the detection of renal calculi.
For detecting urinary calculi, the sensitivity and specificity of IVU are 52% One of the advantages of IVU over CT is its ability to detect intraluminal filling defects and mucosal abnormalities in the renal collecting systems and ureters and 59%, respectively. Excretory-phase collecting system opacification obtained during CT urography was found by McNicholas and colleagues to be comparable to collecting system opacification obtained during IVU.
With advances in CT technology, the technique of CT urography is used to evaluate the entire urinary system.
MDCT enables faster data acquisition and higher resolution images than single-detector helical CT with very thin (approximatley 1-mm) slices The entire urinary system (ie, kidneys, ureters, and bladder) are visualized in one breath-hold on MDCT. Its initial thin data acquisition enables better quality reconstructed and reformatted coronal images similar to those of IVU.
CT urography can demonstrate not only urinary tract lumen but also the walls of the urinary tract and its surrounding structures.
CT urography techniques
The ideal technique for CT urography is unclear and evolving; however, there are two major approaches for CT urography. One of them, a hybrid technique, combines the use of axial CT images with some projection radiographs (conventional filmscreen abdominal radiographs, computed digital radiographs, or CT scanned projection radiographic [SPR] images) after IV contrast medium administration . This method combines the strengths of CT and IVU into a single comprehensive examination. The second approach is CT-only CT urography, which combines conventional axial CT with thinsection, excretory-phase, axial CT images and is reviewed as 2-D and 3-D reformatted images.
CT hybrid urography
This technique combines the advantages of CT in imaging the kidneys with those of contrast radiography in imaging the urinary collecting system; the advantage of this technique is that it does not need CT postprocessing procedures. If CT topography is used, the image quality of a CT topogram to view the urothelium is questionable. If conventional radiography is obtained after the CT scan, patients must undergo imaging in two different locations.
This technique combines the advantages of CT in imaging the kidneys with those of contrast radiography in imaging the urinary collecting system; the advantage of this technique is that it does not need CT postprocessing procedures. If CT topography is used, the image quality of a CT topogram to view the urothelium is questionable. If conventional radiography is obtained after the CT scan, patients must undergo imaging in two different locations.
Movement of patients between different procedure rooms requires additional time and resources, which can cause scheduling conflicts and may affect the level of pyelocalyceal distention at the time of the radiography adversely.
An alternative approach, developed at the Mayo Clinic, solves this problem. An MDCT scanner configured with a special tabletop apparatus is used to obtain CT and radiographic images without moving patients. This tabletop is capable of receiving a combined slip-on grid and standard film cassette. This system requires the installation of a ceilingmounted x-ray tube above the CT table and the attachment of an auxiliary CT tabletop with a hollow bay under the patient surface in which to place the radiographic cassette. With this technique, an abdominal radiograph, an unenhanced renal CT, and a multiphasic, contrastenhanced, renal CT scan followed by overhead excretory urographic and postvoid radiographs can be obtained.
This method permits high spatial resolution IVU film images to be obtained at various times before and after the CT acquisitions, and there is no need to transfer patients between radiography and CT suites.
An alternative method of obtaining projection images, without moving patients from the CT table, is the use of the CT SPR technique (scout view, topogram, or scanogram). The spatial resolution of CT SPR is inferior to that of conventional radiography, whereas the contrast resolution of opacified structures is similar to that of conventional radiography.
This CT urography approach, the combination of helical CT scans and enhanced CT SPR urographic images, is attractive because modification of the CT tabletop and installation of a ceiling-mounted x-ray tube are unnecessary; therefore, this technique can be performed with any MDCT equipment. With this technique, some investigators recommend bowel preparation using a mild laxative to reduce gas and fecal material. To visualize the intrarenal collecting system and ureter better, IVU abdominal compression is applied after the IV contrast medium injection. It is important to use a low-osmolar, iodinated contrast medium.
The ureters generally are well visualized on 10-minute decompressed film images. Twenty-minute and postvoiding films are optional but may be useful for bladder evaluation.
CT-only CT urography This approach is based on the acquisition of unenhanced and enhanced CT scans of the abdomen and pelvis, including the essential acquisition of thinrenal section helical CT scans of the urinary tract during the excretory phase of enhancement.
No bowel preparation is necessary for this type of CT urography. Multiplanar 2-D and 3-D reformation images can be generated on workstations from axial source images obtained during the excretory phase. Detection of urothelial abnormalities with excretory-phase CT requires visualization of the optimally distended and opacified collecting system. Some studies show that CT with abdominal compression improves opacification of the collecting system when compared with CT scans without compression. Caoili and coworkers describe four-phase MDCT urography performed using an unenhanced scan, a nephrographic-phase scan with abdominal compression, and two excretory-phase scans, one obtained 200 seconds after the injection of contrast material with compression and the other 300 seconds after release of compression. They easily identified all congenital anomalies on transverse and 3-D reformatted images. Renal, pelvic, ureteral, and bladder abnormalities are visualized better on compressionrelease excretory-phase images. Three-dimensional images are helpful particularly in the diagnosis of papillary abnormalities, such as renal tubular ectasia and papillary necrosis. Alternative techniques can be used to achieve optimal visualization of the collecting systems, such as normal saline infusion and diuretic injection. CT urography with supplemental saline administration can improve opacification of the distal ureters significantly. Patient position (supine or prone) during CT examination does not affect ureteral visualization.
CT depicts the high attenuation produced by contrast material easily; dilution of the contrast material does not affect perceived opacification and may minimize potential beam-hardening artifacts associated with dense contrast material in the intrarenal collecting system.
The distal ureters are the most difficult segments to opacify; they opacify more reliably if a saline infusion technique is used (250 mL saline chase after the IV contrast administration). Using IV injection of low-dose diuretics (10 mg of furosemide) before IV contrast injection allows less dense, homogeneous opacification of the collecting system. Some investigators use oral water (1000 mL within 15 to 20 minutes) before the examination, as this allows sufficient opacification of the calyces and ureters in most instances.
The authors
do not use an oral bowel contrast agent or water routinely in CT urography protocols. Evaluation of axial CT images (source images) with a wide window setting is important for accurate diagnosis, and these images can be assessed at a workstation. Coronal or oblique MPR images help to define the location and extent of the lesions shown on axial images. MIP images resemble conventional IVU images. CPR allow a single image to outline the course of ureterectasis to the point where an obstructing process, such as a calculus or tumor, is present.
do not use an oral bowel contrast agent or water routinely in CT urography protocols. Evaluation of axial CT images (source images) with a wide window setting is important for accurate diagnosis, and these images can be assessed at a workstation. Coronal or oblique MPR images help to define the location and extent of the lesions shown on axial images. MIP images resemble conventional IVU images. CPR allow a single image to outline the course of ureterectasis to the point where an obstructing process, such as a calculus or tumor, is present.
The authors’ CT urography protocol
The standard CT urography protocol at the authors’ institution is demonstrated in Table below.
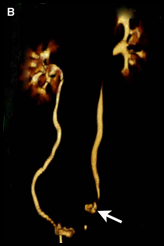
The first phase is precontrast imaging of the abdomen from the dome of the liver to the pubic symphysis using a 3-mm section thickness. The second phase is the nephogram phase that includes imaging from the diaphragm to the iliac crest area with a 2-mm section thickness 100 seconds after starting IV contrast medium followed by 250-mL saline administration. The third phase is the delayed or excretory phase obtained 10 minutes after contrast media administration. After this phase, a scout abdominal CT view. similar to IVU also is obtained. The authors routinely use MPR, MIP, and 3-D VRT postprocessing techniques to assess the acquired axial data. MIP and 3-D VRT images resemble IVU and are preferred by referring physicians (Fig.4B).
Oblique MIP and VRT images are useful for demonstrating distal or tortuous ureteral segments and the ureterovesical junction. Using oblique MIP imaging, phleboliths are easily distinguished from ureteral calculi.
Excretory-phase axial CT image of the pelvis shows contrast medium extravasations in the left distal ureter (arrow). Corresponding coronal VRT.
CT urogram demonstrates contrast leak (arrow) in the left distal ureteral segment.
jurnal radiology Tags: CT urography techniques



Post a Comment for "CT urography"