Ultrasound Images Biliary crystals
Occasionally, echogenic bile persists even with normal gallbladder function (Fig. A). The significance of this is unclear. It has been suggested that here is a spectrum of biliary disease in which gallbladder dysmotility and subsequent saturation of the bile lead to the formation of crystals in the bile and also in the gallbladder wall, leading eventually to stone formation. Pain and biliary colic may be present prior to stone formation and the presence of echogenic bile seems to correlate with the presence of biliary crystals. Biliary crystals, or ‘microlithiasis’ (usually calcium bilirubinate granules) have a strong association with acute pancreatitis43 and its presence in patients who do not have gallstones is therefore highly significant.
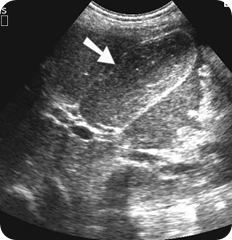
Biliary crystals.
viscous and hyperechoic. The biliary ducts remain normal in calibre. Eventually the bile turns watery and appears echo-free on ultrasound; this is known as a mucocoele (see BELOW ) FIG B. Bile stasis within the ducts occurs either as a result of prolonged and/or repetitive obstruction or as a result of cholestatic disease such as primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) (Chapter 4) or PSC. This can lead to cholangitis.

FIG. B
Wonderful Radiology Blog! I found it while browsing on Yahoo News. Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Many thanks
ReplyDeleteyou can check out article about Fast Ultrasound here: http://radiologydefinition.com/fast-ultrasound-focused-assessment-sonography-trauma/