Glutaric aciduria type I : MRI
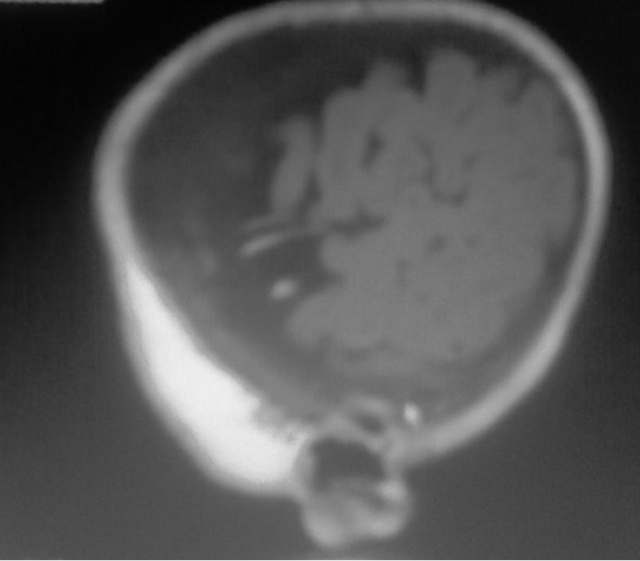
Case Report: 4 month old female child diagnosed as Glutaryl aciduria type 1 , displays correlative MRI findings in the form of grossly expansile convexity subarachnoid spaces with possible arachnoid cysts in left presylvian spaces ( aetiology of prominent space due to under opercularization or arachnoid cysts per say ,not known) ) with symmetrical bright signal intensity lesions of basal ganglia with reduced ADC values with rest normal for age
Teaching points by Dr MGK Murthy, MRI technician Mr Sudhakar
1. a variety of autosomal recessive aetiology leukodystrophy with Glutaryl -CoA dehydrogenase deficiency , leading to accumulation of glutaric acid and 3 hydroxy glutaric acid in brain and body fluids ( detected in urine for diagnosis either continuously or intermittently during decompensation episodes)
2.MRI is described as typical with
(a) Basal ganglia swelling (restricted diffusion) initially and later necrosis/ atrophy
(b) Substantia nigra/ dentate nucleus may be affected
(c) Expanded subarachnoid spaces anterior to sylvian fissure ( whether arachnid cysts or prominent spaces due to under opercularization not known)
(d) Tegmental tracts along the 4 th ventricle floor may be bright on DW
(e) Expanded subabrachnoid spaces put pressure on bridging veins , may lead to hematomata/ hygromata
(f) Delayed myelination
3. Though MRI is not diagnostic , extrapyramidal symptoms in macrocephalic child with MRI findings as above should warrant body fluids examination for glutaric acid ( can also present as acute encephalopathy)
4. Slowly progressive and fatal in 1 st decade unless treated early(without metabolic crisis i.e.. basal ganglia lesions) unless early treatment with low protein diet,carnitine and riboflavine supplements) started





Post a Comment for "Glutaric aciduria type I : MRI"