ULTRASOUND IMAGES CHOLELITHIASIS
Not automatically be assumed that, when gallstones are present, they are responsible for the pain. It is not uncommon to find further pathology in the presence of gallstones and a comprehensive upperabdominal survey should always be carried out.
Gallstones are associated with a number of conditions. They occur when the normal ratio of components making up the bile is altered, most commonly when there is increased secretion of cholesterol in the bile. Conditions which are associated with increased cholesterol secretion, and therefore the formation of cholesterol stones, include obesity, diabetes, pregnancy and oestrogen therapy. The incidence of stones also rises with age, probably because the bile flow slows down.
An increased secretion of bilirubin in the bile, as in patients with cirrhosis for example, is associated with pigment (black or brown) stones. The most commonly and reliably identified gallbladder pathology is that of gallstones (see Table 3.1). More than 10% of the population of the UK have gallstones. Many of these are asymptomatic, which is an important point to remember.
Gallstones are associated with a number of conditions. They occur when the normal ratio of components making up the bile is altered, most commonly when there is increased secretion of cholesterol in the bile. Conditions which are associated with increased cholesterol secretion, and therefore the formation of cholesterol stones, include obesity, diabetes, pregnancy and oestrogen therapy. The incidence of stones also rises with age, probably because the bile flow slows down.
An increased secretion of bilirubin in the bile, as in patients with cirrhosis for example, is associated with pigment (black or brown) stones. The most commonly and reliably identified gallbladder pathology is that of gallstones (see Table 3.1). More than 10% of the population of the UK have gallstones. Many of these are asymptomatic, which is an important point to remember.
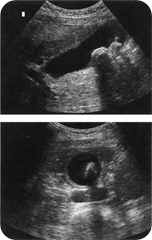
(A) Longitudinal section and (B) transverse
section images of the gallbladder containing stones with
strong distal acoustic shadowing. Note the thickened
gallbladder wall.
section images of the gallbladder containing stones with
strong distal acoustic shadowing. Note the thickened
gallbladder wall.
Table 3.1 Gallstones—clinical features Often asymptomatic
Biliary colic—RUQ pain, fatty intolerance
+ve ultrasound Murphy’s sign (if inflammation is present)
Recurring (RUQ) pain in chronic cholecystitis
Jaundice (depending on degree of obstruction)
Fluctuating fever (if infection is present)
RUQ=right upper quadrant.
Biliary colic—RUQ pain, fatty intolerance
+ve ultrasound Murphy’s sign (if inflammation is present)
Recurring (RUQ) pain in chronic cholecystitis
Jaundice (depending on degree of obstruction)
Fluctuating fever (if infection is present)
RUQ=right upper quadrant.
LiveJournal Tags: ULTRASOUND IMAGES CHOLELITHIASIS
Post a Comment for "ULTRASOUND IMAGES CHOLELITHIASIS"